Hey there, Lumbung Dana! Ever felt like your software application is bursting at the seams, struggling to keep up with growing user demands? You’re not alone. As businesses expand, their software needs to scale accordingly. Traditional monolithic architectures often falter under this pressure, leading to performance bottlenecks and frustrated users. That’s where microservices come in. This article dives deep into how microservices architecture improves software scalability, offering a flexible and robust solution for modern applications.
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, scalability is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Microservices offer a powerful approach to achieving this, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands and maintain optimal performance. Let’s explore this fascinating architectural style and discover how it can transform your software development process.
Understanding Microservices Architecture
What are Microservices?
Microservices architecture is a development approach where an application is structured as a collection of loosely coupled, independently deployable services. Each service focuses on a specific business capability and communicates with other services via lightweight mechanisms, often an HTTP-based API. Think of it like building with LEGOs: each brick (microservice) has a specific function and can be combined with others to create a complex structure (application).
Monolithic vs. Microservices: A Scalability Showdown
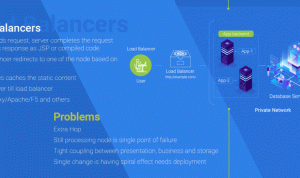
Traditional monolithic architectures, where all application components are tightly interconnected, often struggle to scale efficiently. Changing one part of the application can impact others, leading to complex deployments and potential downtime. Microservices, on the other hand, allow for independent scaling of individual services. If one service experiences increased demand, you can scale only that service without affecting the rest of the application. This targeted scalability significantly improves resource utilization and overall application performance.
Scalability Benefits of Microservices
Independent Scaling: The Power of Isolation
One of the key advantages of microservices architecture is independent scaling. As mentioned earlier, you can scale specific services based on their individual needs. Imagine your e-commerce platform experiences a surge in traffic during a flash sale. With microservices, you can scale the order processing service independently, ensuring smooth checkout for all customers without impacting other functionalities like product browsing or user authentication.
Resource Optimization: Doing More with Less
By scaling only the necessary services, microservices architecture allows for efficient resource utilization. You avoid wasting resources on scaling entire applications when only specific parts are under pressure. This granular control over resource allocation translates to cost savings and improved overall system efficiency. How Microservices Architecture Improves Software Scalability becomes evident when observing this efficient resource management.
Fault Isolation: Containing the Damage
Another crucial benefit of microservices is fault isolation. If one service fails, the impact is contained within that service, preventing a cascading failure that could bring down the entire application. This resilience is particularly important in complex systems where dependencies between components can be intricate. This is yet another example of how microservices architecture improves software scalability and robustness.
Implementing Microservices for Scalability
Choosing the Right Technology Stack
Selecting the appropriate technology stack is vital for successful microservices implementation. Consider factors like language, framework, and database choices based on the specific needs of each service. The flexibility offered by microservices allows you to choose the best tool for the job, optimizing performance and development efficiency.
API Management: Connecting the Dots
Effective API management is crucial for communication between microservices. A well-defined API gateway acts as a central point of entry for requests, routing them to the appropriate services and enforcing security policies. This centralized management simplifies communication and ensures consistent behavior across the application. This is an important factor in how microservices architecture improves software scalability by simplifying complex interactions.
Monitoring and Logging: Keeping an Eye on Things
In a distributed microservices environment, monitoring and logging are essential. Comprehensive monitoring tools provide insights into service performance, enabling proactive identification and resolution of potential issues. Detailed logging helps track down errors and understand system behavior, contributing to improved stability and maintainability. This observability is key to understanding how microservices architecture improves software scalability in real-world scenarios.
Microservices Scalability: A Table Breakdown
| Feature | Monolithic Architecture | Microservices Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Limited, entire application needs to scale | Independent, individual services can scale |
| Fault Tolerance | Single point of failure | Isolated failures, increased resilience |
| Deployment | Complex, often requires downtime | Independent deployments, faster release cycles |
| Technology Stack | Limited flexibility | Greater flexibility, choose the best tool for each service |
| Complexity | Lower initial complexity, higher long-term complexity | Higher initial complexity, lower long-term complexity |
Conclusion
How Microservices Architecture Improves Software Scalability is a complex yet crucial topic for modern application development. By embracing the principles of loose coupling, independent deployment, and targeted scaling, microservices enable businesses to build resilient, adaptable, and high-performing applications. We’ve explored the various facets of this architectural style and how it addresses the challenges of scalability in today’s dynamic digital landscape. We encourage you to check out our other articles on related topics, including best practices for microservices implementation and strategies for managing complex distributed systems. Thanks for reading, Lumbung Dana!
FAQ about How Microservices Architecture Improves Software Scalability
What are microservices?
Microservices are a software architecture style where an application is structured as a collection of loosely coupled, independently deployable services. Think of it like building with LEGOs – each brick (microservice) has a specific function and can be combined with others to create a larger structure (application).
How is it different from a monolithic architecture?
Monolithic architecture is like a giant cake – everything is baked together. Microservices, on the other hand, are like individual cupcakes – each one self-contained.
How do microservices improve scalability?
By breaking down the application into smaller, independent services, you can scale specific parts of your application that need more resources without scaling the entire thing. This is more efficient and cost-effective.
Can you give an example of scaling with microservices?
Imagine an e-commerce site. During a flash sale, the order processing service might experience a surge in traffic. With microservices, you can scale only the order processing service to handle the increased load, leaving other services like product browsing unaffected.
What are the benefits of independent deployment?
Independent deployment means you can update or fix individual services without affecting others. This allows for faster release cycles and reduces the risk of large-scale outages.
How does loose coupling contribute to scalability?
Loose coupling means services are not heavily dependent on each other. This allows them to scale independently and makes the system more resilient to failures in individual services.
Are microservices always the best choice?
Not necessarily. Microservices introduce complexity in managing and monitoring the individual services. For smaller applications, a monolithic architecture might be simpler and more efficient.
Is there a learning curve associated with microservices?
Yes, there’s a learning curve involved in understanding and implementing microservices effectively. It requires understanding distributed systems concepts and choosing appropriate technologies.
What tools and technologies are used with microservices?
Common tools and technologies include Docker for containerization, Kubernetes for orchestration, API gateways for routing traffic, and message queues for inter-service communication.
How do I get started with microservices?
Start by identifying key functionalities within your application that can be separated into independent services. Then, research and choose appropriate technologies for your specific needs. Start small and gradually migrate to a microservices architecture.